-
How Much Does It Cost to Build an Amazon Marketplace Business in 2023
How Much Does It Cost to Build an Amazon Marketplace Business in 2023?

If you are dreaming of launching your own online marketplace like Amazon, you might be wondering how much it will cost you to make it happen. In this blog post, we will try to give you a clear perspective on the estimated cost of building an Amazon marketplace business in 2023, including mobile app, backend, support, IT department, cloud computing expenses, etc.
What is an online marketplace?
An online marketplace is a platform that connects buyers and sellers of various goods and services. It acts as an intermediary that facilitates transactions and earns commissions or fees from each sale. Some examples of popular online marketplaces are eBay, Etsy, Airbnb, Uber, and of course, Amazon.
What are the benefits of building an online marketplace?
Building an online marketplace can be a lucrative and rewarding venture for entrepreneurs who want to tap into the growing e-commerce market. Some of the benefits of building an online marketplace are:
- You can offer a wide range of products and services from different categories and niches, attracting more customers and increasing your revenue potential.
- You can leverage the existing supply and demand of the market, without having to worry about inventory, logistics, or fulfillment.
- You can create a loyal community of buyers and sellers who trust your platform and provide feedback, reviews, and referrals.
- You can scale your business easily by adding new features, categories, or regions to your platform.
What are the challenges of building an online marketplace?
Building an online marketplace is not a walk in the park. It requires a lot of planning, research, development, testing, marketing, and maintenance. Some of the challenges of building an online marketplace are:
- You must compete with established players who have a large customer base, brand recognition, and market share.
- You must ensure the quality and security of your platform, as well as the satisfaction and safety of your users.
- You must comply with various laws and regulations that govern e-commerce, taxation, privacy, data protection, etc.
- You must invest a significant amount of time and money to build and grow your platform.
How much does it cost to build an online marketplace like Amazon in 2023?
The cost of building an online marketplace like Amazon in 2023 depends on many factors, such as:
- The type and scope of your platform: Do you want to build a vertical or horizontal marketplace? Do you want to focus on a specific niche or category? Do you want to offer local or global services? Do you want to support multiple languages and currencies?
- The features and functionality of your platform: What are the essential and advanced features that you want to include in your platform? How complex and customized do you want them to be? Do you want to integrate third-party services or APIs?
- The design and user experience of your platform: How do you want your platform to look and feel? How do you want to optimize it for different devices and screen sizes? How do you want to enhance its usability and accessibility?
- The technology stack and development approach of your platform: What are the tools and frameworks that you want to use to build your platform? How do you want to structure your backend and frontend architecture? How do you want to manage your data storage and processing? How do you want to test and deploy your platform?
- The team and timeline of your project: Who are the people that you need to hire or collaborate with to build your platform? What are their roles and responsibilities? How much do they charge for their services? How long will it take them to complete the project?
Based on these factors, the cost of building an online marketplace like Amazon in 2023 can vary greatly from $40,000 to $400,000 or more. However, this is just a rough estimate that can change depending on the specific requirements and expectations of each project.
To give you a more realistic idea of how much it will cost you to build an Amazon marketplace business in 2023, let’s break down some of the major expenses that you will have to incur:
Mobile app development
According to Statista, mobile e-commerce sales are expected to reach $3.56 trillion in 2021, accounting for 72.9% of total e-commerce sales. Therefore, having a mobile app for your online marketplace is not optional; it’s mandatory.
The cost of developing a mobile app for your online marketplace depends on the platform (iOS or Android), the features (basic or advanced), the design (standard or custom), and the development team (in-house or outsourced).
According to Codica , a basic mobile app for an online marketplace can cost around $20,000-$40,000 per platform. However, if you want to add more advanced features such as geolocation, push notifications, chat, ratings and reviews, payment gateways, etc., the cost can go up to $80,000-$120,000 per platform.
Backend development
The backend of your online marketplace is the engine that powers your platform. It handles the business logic, data storage, security, performance, scalability, and integration of your platform.
The cost of developing a backend for your online marketplace depends on the technology stack, the database, the cloud service provider, the APIs, and the development team.
According to Codica , a basic backend for an online marketplace can cost around $20,000-$40,000. However, if you want to add more complex functionalities such as search and filtering, recommendations, analytics, etc., the cost can go up to $80,000-$120,000.
Support
Support is an essential part of running an online marketplace. You need to provide customer service, technical support, dispute resolution, fraud prevention, and quality assurance to your users.
The cost of providing support for your online marketplace depends on the number of users, the number of transactions, the type and level of service, and the support team.
According to Jungle Scout, a basic support service for an online marketplace can cost around $500-$1,000 per month. However, if you want to provide more comprehensive and professional service such as phone support, live chat, email support, etc., the cost can go up to $5,000-$10,000 per month.
IT department
IT department is responsible for maintaining and updating your online marketplace. You need to have a team of developers, testers, designers, and managers who can fix bugs, add new features, improve performance, and ensure security of your platform.
The cost of having an IT department for your online marketplace depends on the size and skill of your team, the complexity and frequency of your updates, and the development approach.
According to Appinventiv , a basic IT department for an online marketplace can cost around $5,000-$10,000 per month. However, if you want to have a more experienced and dedicated team who can work on agile methodology and deliver faster and better results, the cost can go up to $20,000-$40,000 per month.
Cloud computing expenses
Cloud computing is a service that allows you to store and access your data and applications over the internet. It offers many benefits such as scalability, reliability, security, and cost-efficiency for your online marketplace.
The cost of using cloud computing for your online marketplace depends on the cloud service provider (Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Microsoft Azure), the cloud service model (Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS)), and the cloud resources (storage space, bandwidth usage, computing power).
A basic cloud computing service for an online marketplace can cost around $3,000-$20,000 per month. However, if you want to use more advanced and specialized services such as machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics etc., the cost can go up to $1,000-$5,000 per month.
Conclusion
Building an online marketplace like Amazon in 2023 is not a cheap or easy endeavor. It requires a lot of planning,
research, development, testing, marketing, and maintenance. However, it also offers a lot of opportunities, rewards, and benefits for entrepreneurs who want to create their own e-commerce empire.Based on our analysis, the estimated cost of building an Amazon marketplace business in 2023 can range from $40,000 to $400,000 or more, depending on various factors such as:
- The type and scope of your platform
- The features and functionality of your platform
- The design and user experience of your platform
- The technology stack and development approach of your platform
- The team and timeline of your project
Of course, this is just a rough estimate that can change depending on the specific requirements and expectations of each project. Therefore, we recommend that you consult with professional developers, designers, and marketers who can help you create a realistic budget and timeline for your online marketplace project.
We hope that this blog post has given you a clear perspective on how much it will cost you to build an Amazon marketplace business in 2023.
: https://www.codica.com/blog/how-much-does-it-cost-to-build-marketplace-website/
: https://www.junglescout.com/blog/how-much-money-do-i-need-to-start-selling-on-amazon/
: https://appinventiv.com/blog/cost-to-develop-a-marketplace-app/
: https://www.mastersofmarketplace.com/real-costs-of-starting-an-amazon-store -
Uber business with a little $300 investment?
How to Build an Uber Business: The Real Cost of Developing a Ride-Hailing App

If you are thinking of creating your own ride-hailing app like Uber, you might be wondering how much it would cost to develop such a project. You might also be tempted by some of the low-cost offers you can find online, promising to deliver a clone of Uber for as little as $300. However, before you jump into such a deal, you should be aware of the reality behind these claims and the actual cost of building a high-quality, scalable and secure app like Uber.
In this blog post, we will break down the main components of a ride-hailing app, the estimated hours and rates of senior IT staff from Upwork in 2023, and the total cost of developing an Uber-like app for both iOS and Android platforms. We will also provide a clear perspective to a naive internet user that believes they can hire someone to make a clone of the end-user app for $300 and then sit back and become a multi-millionaire by doing nothing with a little investment of $300.
What are the main components of a ride-hailing app?
A ride-hailing app like Uber consists of several components that work together to provide a seamless user experience. These components are:
A mobile app for passengers: This is the app that allows users to request rides, see the location and details of their drivers, pay for their trips, rate their drivers, and access other features such as ride history, promotions, referrals, etc.
- A mobile app for drivers: This is the app that allows drivers to accept or decline ride requests, see the location and details of their passengers, navigate to their destinations, receive payments, rate their passengers, and access other features such as earnings, feedback, support, etc.
- A backend system: This is the server-side part of the app that handles the business logic, data storage, communication between the apps, authentication, security, payment processing, etc.
- A web-based admin panel: This is the web interface that allows the app owners or administrators to manage the app operations, such as adding or removing drivers, setting fares and commissions, monitoring transactions and ratings, generating reports and analytics, etc.
- A cloud computing service: This is the service that provides the infrastructure and resources to host and run the backend system and the admin panel on the internet.
How much does it cost to hire senior IT staff from Upwork in 2023?
According to various sources, the average hourly rate of senior IT staff from Upwork in 2023 ranges from $50 to $200 per hour depending on the country they are based in. For example:
- In India, the average hourly rate is $50 per hour
- In Ukraine, the average hourly rate is $75 per hour
- In Canada, the average hourly rate is $100 per hour
- In the US, the average hourly rate is $150 per hour
- In Australia, the average hourly rate is $200 per hour
Of course, these are only averages and there might be variations depending on the skills, experience, and reputation of each individual freelancer. However, for simplicity’s sake, we will use these averages as our reference points.
How many hours does it take to develop an Uber-like app?
The number of hours required to develop an Uber-like app depends on many factors such as:
- The complexity and scope of the features
- The quality and performance standards
- The design and user interface
- The testing and debugging process
- The maintenance and support
However, based on some estimates, we can assume that it would take around 1,600 hours to develop a basic version of an Uber-like app for both iOS and Android platforms. This includes:
- 500 hours for the passenger app
- 500 hours for the driver app
- 400 hours for the backend system
- 200 hours for the admin panel
Of course, this is only a rough estimate, and it might vary depending on the specific requirements and specifications of each project.
How much does it cost to develop an Uber-like app?
Based on our previous assumptions, we can calculate the total cost of developing an Uber-like app by multiplying the number of hours by the hourly rate of each country. For example:
- In India: 1,500 x $50 = $75,000
- In Ukraine: 1,500 x $75 = $112,500
- In Canada: 1,500 x $100 = $150,000
- In the US: 1,500 x $150 = $225,000
- In Australia: 1,500 x $200 = $300,000
These are only the development costs and they do not include other expenses such as:
- Cloud computing service fees
- Payment gateway fees
- Marketing and promotion costs
- Legal and licensing fees
- Taxes and commissions
Therefore, the actual cost of launching and running an Uber-like app might be much higher than these estimates.
Why is it impossible to create an Uber clone for $300?
As you can see from the above calculations, it is impossible to create an Uber clone for $300. Anyone who claims to do so is either lying, defrauding, or delivering a low-quality product that will not meet your expectations or the standards of the market.
Some of the reasons why it is impossible to create an Uber clone for $300 are:
- It takes a lot of time and effort to develop a complex and sophisticated app like Uber. You cannot expect to get a high-quality product in a short time and on a low budget.
- It requires a team of skilled and experienced professionals to develop an Uber-like app. You cannot rely on one person or a cheap freelancer to handle all the aspects of the project.
- It involves a lot of technical challenges and risks to develop an Uber-like app. You cannot ignore the security, scalability, performance, reliability, and compatibility issues that might arise during the development process.
- It demands a lot of maintenance and support to run an Uber-like app. You cannot neglect the updates, bug fixes, enhancements, and customer service that are essential for the success of your app.
Therefore, if you are serious about creating your own ride-hailing app like Uber, you should be prepared to invest a significant amount of money, time, and resources into the project. You should also be realistic about your expectations and goals and do your research before hiring any developers or freelancers.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we have explained the main components of a ride-hailing app like Uber, the estimated hours and rates of senior IT staff from Upwork in 2023, and the total cost of developing an Uber-like app for both iOS and Android platforms. We have also provided a clear perspective to a naive internet user that believes they can hire someone to make a clone of the end-user app for $300 and then sit back and become a multi-millionaire by doing nothing with a little investment of $300.
We hope that this blog post has been informative and helpful for you. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to contact us. We would love to hear from you.
-
Frontend framework WAR: Angular, React, Vue, and jQuery
Frontend framework WAR
Angular, React, Vue, and jQuery are four popular JavaScript frameworks or libraries that can create dynamic and interactive web applications. This article will compare them based on various criteria, such as their features, performance, popularity, support, learning curve, advantages and disadvantages, and some examples of well-known applications built with them. We will also discuss what companies are behind these frameworks and what developers can expect from them. Finally, we will give some recommendations on which framework is best for what scenario.
Features

Angular is a full-fledged front-end framework that provides a complete solution for building single-page applications (SPAs). It follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern and supports two-way data binding, dependency injection, routing, testing, and more. Angular uses TypeScript, a superset of JavaScript that adds static typing and other features.

React is a UI library that focuses on rendering components efficiently. It uses a virtual DOM to update the UI without affecting the actual DOM. React also supports one-way data binding, hooks, custom elements, server-side rendering, and more. React uses JavaScript with JSX, an extension that allows embedding XML in the code.

Vue is a progressive framework that can be used to create simple or complex web applications. It is inspired by Angular and React and combines some of their best features. Vue supports reactive data binding, directives, transitions, routing, state management, and more. Vue uses a templating syntax that is similar to HTML but with special attributes and expressions.

jQuery is a lightweight library that simplifies DOM manipulation, event handling, animation, Ajax, and more. jQuery is not a framework but rather a collection of useful methods that can be used with plain JavaScript or other frameworks. jQuery uses a fluent syntax that makes it easy to chain multiple operations.
Performance
Performance is an important factor to consider when choosing a framework or library for web development. Performance depends on various factors, such as the size of the codebase, the complexity of the logic, the number of DOM elements, the browser compatibility, and more. Therefore, it is not easy to compare the performance of different frameworks or libraries in a general way.
However, some benchmarks have been conducted to measure the performance of Angular, React, Vue, and jQuery in specific scenarios, such as creating or updating rows in a table, selecting rows, swapping rows, removing rows, etc. The results of these benchmarks show that they all perform quite well at most tasks, but there are some differences.
According to the JS Framework Benchmark , Vue is considerably slower than Angular and React at selecting rows. React is slightly faster than Angular at creating rows but slightly slower at appending rows. Angular is faster than React and Vue at swapping rows but slower at removing rows. jQuery is slower than all three frameworks at most tasks except selecting rows.
According to the RealWorld Benchmark , Angular has the largest codebase size among the four frameworks or libraries. React has the smallest codebase size but requires additional libraries for routing and state management. Vue has a moderate codebase size but also requires additional libraries for routing and state management. jQuery has the smallest codebase size but does not provide any structure or features for building complex applications.
Popularity
Popularity is another factor to consider when choosing a framework or library for web development. Popularity indicates how widely used and supported a framework or library is by developers and companies. Popularity can be measured by various metrics, such as the number of downloads, stars, forks, contributors, issues, etc. on GitHub or npm.
According to npm trends , React has the highest number of downloads among the four frameworks or libraries in the past year. Vue has the second-highest number of downloads followed by jQuery and Angular. However, jQuery has the highest number of downloads in total since it has been around longer than the other three frameworks or libraries.
According to GitHub , React has the highest number of stars among the four frameworks or libraries followed by Vue and Angular. jQuery has the lowest number of stars but has the highest number of forks. React also has the highest number of contributors followed by Angular and Vue. jQuery has the lowest number of contributors but has the highest number of issues.
Support
Support is another factor to consider when choosing a framework or library for web development. Support indicates how easy it is to find help and resources for learning and troubleshooting a framework or library. Support can be measured by various metrics, such as the availability of documentation, tutorials, courses, forums, stack overflow questions, etc.
According to their official websites, all four frameworks or libraries have comprehensive documentation that covers their features, APIs, examples, guides, etc.
They also have official or community-supported tutorials, courses, books, videos, etc. that can help beginners and advanced developers learn and master them.
According to Stack Overflow , jQuery has the highest number of questions among the four frameworks or libraries followed by Angular and React. Vue has the lowest number of questions but has the highest percentage of answered questions. React has the second-highest percentage of answered questions followed by Angular and jQuery.
Learning curve
Learning curve is another factor to consider when choosing a framework or library for web development. Learning curve indicates how easy or difficult it is to learn and use a framework or library. Learning curve depends on various factors, such as the familiarity of the syntax, the complexity of the concepts, the amount of boilerplate code, the flexibility of the options, etc.
According to most developers:
jQuery has the easiest learning curve among the four frameworks or libraries since it is based on plain JavaScript and has a simple and intuitive syntax. jQuery also has a lot of examples and resources that can help developers get started quickly.
Vue has the second-easiest learning curve among the four frameworks or libraries since it is also based on plain JavaScript and has a templating syntax that is similar to HTML. Vue also has a clear and concise documentation that explains its features and concepts well.
React has a moderate learning curve among the four frameworks or libraries since it uses JavaScript with JSX, which is a syntax extension that allows embedding XML in the code. React also has some advanced concepts, such as hooks, custom elements, server-side rendering, etc. that require more understanding and practice.
Angular has the steepest learning curve among the four frameworks or libraries since it uses TypeScript, which is a superset of JavaScript that adds static typing and other features. Angular also has a complex structure and architecture that follows the MVC pattern and requires more configuration and boilerplate code.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages and disadvantages are another factor to consider when choosing a framework or library for web development. Advantages and disadvantages indicate the pros and cons of using a framework or library for building web applications. Advantages and disadvantages depend on various factors, such as the features, performance, popularity, support, learning curve, etc. of each framework or library.
According to most developers, some of the advantages and disadvantages of each framework or library are:
Angular
Advantages:
- Provides a complete solution for building SPAs with features such as routing, testing, dependency injection, etc.
- Supports two-way data binding that synchronizes the data between the model and the view automatically
- Uses TypeScript that adds static typing and other features that enhance code quality and readability
- Has a large and active community that provides support and resources
Disadvantages:
- Has a steep learning curve that requires learning TypeScript and Angular-specific concepts
- Has a large codebase size that can affect performance and loading time
- Has a complex structure and architecture that requires more configuration and boilerplate code
- Has frequent updates that can introduce breaking changes
React
Advantages:
- Provides a fast and efficient way of rendering components with features such as virtual DOM, hooks, custom elements, etc.
- Supports one-way data binding that makes the data flow more predictable and easier to debug
- Uses JavaScript with JSX that allows writing HTML-like code in JavaScript
- Has a huge and active community that provides support and resources
Disadvantages:
- Requires additional libraries for routing, state management, testing, etc.
- Has a moderate learning curve that requires learning JSX and React-specific concepts
- Has some compatibility issues with older browsers
- Has frequent updates that can introduce breaking changes
Vue
Advantages:
- Provides a progressive framework that can be used for simple or complex web applications with features such as reactive data binding, directives, transitions, etc.
- Supports both templating syntax and raw JavaScript or JSX for creating components
- Has a small codebase size that improves performance and loading time
- Has a clear and concise documentation that explains its features and concepts well
Disadvantages:
- Requires additional libraries for routing, state management, testing, etc.
- Has a smaller community than Angular or React that provides less support and resources
- Has some compatibility issues with older browsers
- Has less market share than Angular or React that affects its demand
jQuery
Advantages:
- Provides a lightweight library that simplifies DOM manipulation, event handling, animation, Ajax, etc.
- Uses plain JavaScript that is familiar to most developers
- Has a simple and intuitive syntax that makes it easy to chain multiple operations
- Has a huge and active community that provides support and resources
Disadvantages:
- Does not provide any structure or features for building complex applications
- Has a low performance compared to modern frameworks or libraries
- Has some compatibility issues with newer browsers
- Has less market share than modern frameworks or libraries that affects its demand
Examples of well-known applications built with each framework or library are:
Angular
- Google AdWord: Google’s online advertising platform uses Angular to handle its complex user interface requirements.
- Upwork: The freelance marketplace utilizes Angular for various parts of its web application, ensuring a fluid user experience.
- Weather.com: The weather forecasting service takes advantage of Angular’s features to present real-time data efficiently.
React
– Facebook: Created and maintained by Facebook, React is also used extensively throughout the company’s products, including the main Facebook app and Instagram.
– Airbnb: The popular home rental service utilizes React to provide users with an interactive and responsive platform.
– Netflix: The streaming giant relies on React for its performance and modularity, enabling a seamless viewing experience.
Vue
–Alibaba: The e-commerce giant utilizes Vue for its front-end development, benefiting from its simplicity and efficiency.
– Xiaomi: The Chinese electronics company leverages Vue to craft user-friendly interfaces across various platforms.
– Grammarly: The online writing assistant uses Vue to create a responsive and intuitive experience for its users.
jQuery
– Twitter: Before adopting other solutions, Twitter utilized jQuery for various functionalities, emphasizing simplicity and compatibility.
– Microsoft: Various Microsoft products have been known to incorporate jQuery, taking advantage of its ease of use.
– IBM: The tech giant has employed jQuery in several web solutions, appreciating its straightforward approach to handling everyday web tasks.
Companies Behind These Frameworks
- Angular: Developed and maintained by Google, ensuring constant updates and strong community support.
- React: Created by Facebook, providing a guarantee of ongoing development, innovation, and extensive community engagement.
- Vue: Initiated by a former Google engineer, Evan You, Vue is now maintained by him and the open-source community, making it an independent project.
- jQuery: Created by John Resig, jQuery has been maintained by a team of open-source contributors, making it platform agnostic.
Recommendations
Choosing the proper framework or library depends on various factors, including project requirements, team expertise, and long-term goals.
- For Large-scale, Complex Applications: Angular might be preferable, thanks to its comprehensive toolset and strong typing through TypeScript.
- For Modern, Component-based Development: React is well-suited, especially with its thriving ecosystem and focus on component reusability.
- For Progressive, Flexible Development: Vue offers a balanced approach and can be a great choice for projects that require a smooth learning curve with powerful features.
- For Simplicity and Quick Prototyping: jQuery, though somewhat dated, can still be effective for simple tasks and smaller projects that don’t require the complexities of full-fledged frameworks.
Conclusion
Angular, React, Vue, and jQuery each offer unique strengths and weaknesses that cater to different project needs. Understanding these frameworks’ features, performance, popularity, and support will help developers and organizations make informed decisions tailored to their specific scenarios. Continually evaluating and adapting to the evolving web development landscape ensures that the right tools are chosen for the right tasks, leading to successful and efficient application development.
-
How Much Does It Cost to Build an MLM Software for a Startup?
How Much Does It Cost to Build an MLM Software for a Startup?

If you are thinking of starting a multi-level marketing (MLM) business, you might be wondering how much it would cost to build MLM software that can handle all the aspects of your business, such as recruiting, commission, inventory, sales, etc. You might also be tempted to look for cheap solutions online that promise to create a clone of a successful MLM app for a fraction of the price. However, before you make any decisions, you should be aware of the reality and complexity of developing MLM software from scratch, and the factors that affect the cost.
In this article, we will provide a clear perspective to a naive internet user that believes they can hire someone to make a clone of the end-user app by US$10k and then will seat and become multi-million self-made by doing nothing with a little invest of $10k dollars. We will also give you an estimate of the cost of building an MLM software for a startup, including mobile app, backend, support, database administrator, scrum master, quality assurance, cloud computing expenses, etc.
What is MLM Software?
MLM software is a software system that enables MLM businesses to manage their operations, such as recruiting new members, tracking sales and commissions, managing inventory and orders, communicating with customers and distributors, etc. MLM software can also provide features such as analytics, reporting, marketing tools, e-commerce integration, etc.
MLM software can be divided into two main components: the front-end and the back-end. The front-end is the user interface that customers and distributors use to interact with the MLM business. It can be a website or a mobile app that allows them to sign up, buy products, view their earnings, etc. The back-end is the server-side application that handles the business logic and data processing of the MLM business. It can be hosted on a cloud platform or on-premises servers.
The Complexity of Developing an MLM Software from Scratch
Developing MLM software from scratch is not a simple task. It requires a lot of planning, design, coding, testing, debugging, deployment, maintenance, and support. It also involves multiple technologies, platforms and frameworks that need to work together seamlessly.
Some of the challenges and complexities of developing an MLM software from scratch are:
- Choosing the right architecture and technology stack for the front-end and back-end
- Designing a scalable and secure database schema that can handle large amounts of data and transactions
- Implementing various MLM compensation plans and algorithms that calculate commissions and bonuses accurately
- Integrating with third-party services and APIs such as payment gateways, e-commerce platforms, SMS providers, etc.
- Ensuring cross-platform compatibility and responsiveness for different devices and browsers
- Testing and debugging the software for functionality, performance, security, and usability
- Deploying and hosting the software on a reliable cloud platform or on-premises servers
- Providing ongoing maintenance and support for bug fixes, updates, and enhancements
The Cost of Building an MLM Software for a Startup
The cost of building an MLM software for a startup depends on various factors such as:
- The scope and complexity of the project
- The features and functionality required
- The design and user experience desired
- The technology stack and platform chosen
- The development team size and expertise
- The development time frame and deadline
- The quality standards and testing methods
- The deployment and hosting options
- The maintenance and support services
Based on these factors, the cost of building an MLM software for a startup can vary widely from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars. However, to give you a rough idea, we will use some assumptions and averages to estimate the cost.
According to Upwork, the average hourly rate of senior IT staff in 2023 is $88 per hour. Assuming that you need a team of 5 developers (2 front-end developers, 2 back-end developers and 1 full-stack developer), 1 designer, 1 database administrator (DBA), 1 scrum master (project manager), 1 quality assurance (QA) engineer and 1 support engineer to build your MLM software from scratch in 6 months (26 weeks), the cost would be:
Project Staffing Costs Breakdown:
1. Front-end Developer:
- Hourly Rate: $88
- Hours/Week: 40
- Weeks: 26
- Total Cost: $91,520
2. Back-end Developer:
- Hourly Rate: $88
- Hours/Week: 40
- Weeks: 26
- Total Cost: $91,520
3. Full-stack Developer:
- Hourly Rate: $88
- Hours/Week: 40
- Weeks: 26
- Total Cost: $91,520
4. Designer:
- Hourly Rate: $88
- Hours/Week: 40
- Weeks: 26
- Total Cost: $91,520
5. DBA (Database Administrator):
- Hourly Rate: $88
- Hours/Week: 40
- Weeks: 26
- Total Cost: $91,520
6. Scrum Master:
- Hourly Rate: $88
- Hours/Week: 40
- Weeks: 26
- Total Cost: $91,520
7. QA (Quality Assurance) Engineer:
- Hourly Rate: $88
- Hours/Week: 40
- Weeks: 26
- Total Cost: $91,520
8. Support Engineer:
- Hourly Rate: $88
- Hours/Week: 40
- Weeks: 26
- Total Cost: $91,520
Overall Total Cost for the Project: $732,160
This is just the development cost. You also need to consider the cost of cloud computing expenses, such as hosting, storage, bandwidth, etc. According to AWS, the average cost of cloud computing for a small business in 2023 is $0.10 per GB per month. Assuming that your MLM software needs 100 GB of storage and 1000 GB of bandwidth per month, the cost would be:
Service Cost per GB per Month GB per Month Months Total Cost Storage $0.10 100 6 $60 Bandwidth $0.10 1000 6 $600 Total – – – $660 Therefore, the total cost of building an MLM software for a startup, including development and cloud computing expenses, would be:
$732,160 + $660 = $732,820
This is a very rough estimate based on some assumptions and averages. The actual cost may vary depending on your specific requirements and circumstances. However, it should give you an idea of the magnitude and complexity of developing MLM software from scratch.
Conclusion
Building MLM software from scratch is not a cheap or easy endeavor. It requires a lot of time, money, expertise and resources. It also involves a lot of risks and challenges that need to be overcome. Therefore, if you are thinking of starting an MLM business, you should not fall for the unrealistic promises of cheap and quick solutions online. Instead, you should do your research and plan your budget carefully. You should also consider hiring a professional and experienced MLM software development company that can provide you with a customized and reliable solution that meets your needs and expectations.
: https://morganoverholt.com/upwork-hourly-rates/
: https://aws.amazon.com/pricing/ -
Flutter vs React Native
Flutter vs React Native: A Comparison of Two Popular Cross-Platform Frameworks

If you are looking for a way to create mobile apps that run on both iOS and Android devices, you might have heard of Flutter and React Native. These are two of the most popular cross-platform frameworks available today, and they are both backed by tech giants: Google and Facebook, respectively.
But what are the advantages and disadvantages of choosing one technology over the other? Which one has more demand right now? What companies are using each technology? What companies are behind those technologies? What reason should a project manager have to pick Flutter over React Native? What labor is easier to hire and what is the average hourly rate for a freelancer and small business to create a project using those technologies?
In this article, we will try to answer these questions by comparing Flutter and React Native in terms of performance, developer experience, ecosystem, device compatibility, and more. Let’s get started!
What is Flutter?
Flutter is a cross-platform UI framework developed by Google. First released in May 2017, Flutter has grown steadily in popularity over the years. One of Flutter’s main selling points is that it enables you to create cross-platform applications using a single codebase.
Traditionally, a company would need multiple tools and developers to create an application that was available on the web, mobile, and desktop. For example, you might need:
- A developer who specializes in web development using React to build the website
- Another developer using C# and Java to create the desktop version.
- A dedicated mobile developer using Kotlin and Swift to build the Android and iOS apps
This approach would require a whole team of developers, not to mention a ton of meetings to make sure the design and branding are consistent across all platforms. You also have to factor in testing for each platform and addressing their respective bugs and quirks.
With Flutter, companies can hire one developer to create apps across platforms with just one codebase to manage. This significantly reduces the time and resources required to launch and maintain an application.
Flutter 3 introduced fairly substantial changes. While the API for writing mobile and web applications hasn’t changed much, you can now use the same codebase to create iPhone, Android, Web, Windows, Mac, and Linux applications using the Flutter Compiler. In addition, Flutter 3 provides better support for Firebase along with a Casual Games Toolkit for creating games with Flutter.
What is React Native?
React Native is another cross-platform framework that allows you to build native-like mobile apps using JavaScript and React. It was created by Facebook in 2015 as an open-source project based on their internal framework for developing mobile apps.
React Native works by using a JavaScript bridge to communicate with native modules that provide access to native features such as camera, location, sensors, etc. This way, you can write your app logic in JavaScript and use native UI components for rendering.
React Native also supports hot reloading and live reloading, which means you can see the changes in your app without rebuilding or restarting it. This makes development faster and more convenient.
React Native has a large and active community of developers who contribute to its core library and create third-party libraries for various functionalities. You can find many resources online to learn React Native or solve any issues you might encounter.
Some of the well-known apps built with React Native include Facebook, Instagram, Skype, Pinterest, Uber Eats, Discord, and Walmart.
Key Differences Between Flutter and React Native
Flutter and React Native share a lot of similarities, but they are also quite different in a handful of keyways. Here are some of the main differences between them:
- Programming language: Flutter uses Dart as its programming language, while React Native uses JavaScript (or TypeScript). Dart is a compiled language that supports both object-oriented and functional paradigms. It also has features such as null safety, generics, mixings, extension methods, etc. JavaScript is an interpreted language that follows a prototype-based inheritance model. It is widely used for web development and has many frameworks and libraries available.
- UI components: Flutter uses its own set of widgets for creating UI elements, while React Native uses native UI components for each platform. Flutter widgets are highly customizable and can adapt to different screen sizes and orientations. They also provide a consistent look and feel across platforms. React Native UI components are more platform-specific and follow the native design guidelines. They also offer better performance and accessibility than Flutter widgets.
- State management: Flutter provides several options for managing state in your app, such as setState(), Provider, Bloc, Riverpod, etc. React Native relies on external libraries for state management, such as Redux, MobX, Recoil, etc. State management is an important aspect of app development that affects how data flows between components and how the app reacts to user actions or external events.
- Documentation: Both Flutter and React Native have extensive documentation that covers the basics and advanced topics of their frameworks. However, Flutter’s documentation is more organized and comprehensive than React Native’s. Flutter’s documentation also includes tutorials, code samples, videos, cookbooks, etc. React Native’s documentation is more scattered and sometimes outdated or incomplete.
- Testing: Flutter has a built-in testing framework that supports unit testing, widget testing, and integration testing. You can also use other tools such as Mockito, Flutter Driver, etc. for mocking and automation. React Native does not have a built-in testing framework, but you can use third-party tools such as Jest, Enzyme, Detox, etc. to test your app. Testing is a crucial part of app development that ensures the quality and reliability of your app.
Flutter vs React Native: Performance
One of the most important factors to consider when choosing a cross-platform framework is performance. How fast and smooth is your app on different devices and platforms? How much memory and CPU does it consume? How does it handle complex animations and transitions?
Performance is often influenced by many factors, such as the programming language, the UI rendering engine, the native bridge, the app architecture, the optimization techniques, etc. Therefore, it is hard to make a general comparison between Flutter and React Native in terms of performance without considering the specific context and use case.
However, based on some common benchmarks and anecdotal evidence, we can say that Flutter has an edge over React Native in performance. Here are some of the reasons why:
- Flutter compiles its Dart code into native code using ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation, which means it runs faster and more efficiently than JavaScript code that is interpreted at runtime.
- Flutter uses its own rendering engine called Skia, which draws everything on a canvas using GPU acceleration. This allows Flutter to achieve high frame rates and smooth animations without relying on native UI components.
- Flutter does not use a JavaScript bridge to communicate with native modules, which means it avoids the overhead and latency of serialization and deserialization of data. Instead, it uses platform channels that are more direct and efficient.
- Flutter supports stateful hot reload and hot restart, which means you can change your code and see the results instantly without losing the app state or restarting the app. This makes development faster and more productive.
React Native, on the other hand, has some performance drawbacks compared to Flutter. Here are some of them:
- React Native runs its JavaScript code on a separate thread using a JavaScript engine such as Hermes or JSCore. This means it has to deal with the performance limitations and inconsistencies of different JavaScript engines on different platforms.
- React Native uses native UI components for rendering, which means it has to synchronize the state of the JavaScript code with the native UI elements using a JavaScript bridge. This can cause performance issues such as jankiness, lagging, or dropped frames when dealing with complex UIs or animations.
- React Native does not support stateful hot reload or hot restart, which means you have to rebuild or restart your app every time you make a change in your code. This can slow down your development process and affect your productivity.
Of course, this does not mean that React Native apps are always slow or unresponsive. There are many ways to optimize your React Native app for better performance, such as using Hermes engine, enabling ProGuard or R8, using FlatList or SectionList instead of ScrollView, using PureComponent or memo for avoiding unnecessary re-rendering, using requestAnimationFrame for animations, etc.
However, these optimizations often require extra work and knowledge from the developer. With Flutter, you get better performance out of the box without much effort.
Flutter vs React Native: Developer Experience
Another factor to consider when choosing a cross-platform framework is developer experience. How easy and enjoyable is it to develop an app using Flutter or React Native? How steep is the learning curve? How much support and resources are available?
Developer experience is subjective and depends on personal preferences and backgrounds. Some developers might prefer one framework over another based on their familiarity with the programming language, the IDE, the tools, etc.
However, based on some common criteria and feedback from developers who have used both frameworks, we can say that Flutter offers a better developer experience than React Native. Here are some of the reasons why:
- Flutter has a lower learning curve than React Native for beginners. If you are new to mobile app development or cross-platform frameworks, you might find Flutter easier to learn than React Native. This is because Flutter has a more consistent and coherent API that follows a declarative approach for creating UIs. You don’t have to deal with multiple concepts such as JSX syntax, props, state, hooks, lifecycle methods, etc. that are common in React Native.
- Flutter has better tooling support than React Native for development. If you use an IDE such as Visual Studio Code or Android Studio for developing your app, you will find that Flutter has better integration and features than React Native. For example, you can use hot reload and hot restart to see your changes instantly without losing state or restarting your app. You can also use Flutter’s DevTools for performance profiling, network inspection, debugging, layout inspection, etc. Flutter’s command-line interface (CLI) also provides useful commands for building, testing, and deploying your app.
- Flutter provides better code organization and architecture than React Native. With Flutter, you can use packages such as Provider, Riverpod, Bloc, etc. to structure your app in a clean and scalable way. You can also use null safety to catch potential bugs at compile-time and write more robust code. React Native relies more on third-party libraries and conventions for managing state, routing, validation, etc., which can be more fragmented and inconsistent.
- Flutter provides more customization and flexibility than React Native for UI design. If you want to create a custom look and feel for your app that goes beyond the native design guidelines, you will find Flutter’s widgets and themes more versatile and powerful than React Native’s components. You can also create custom animations, transitions, gestures, etc. in Flutter using the rich set of APIs and libraries available.
React Native also has its advantages in developer experience, such as the familiarity with JavaScript, the large community of developers, the wide range of third-party libraries, etc. However, React Native also has some challenges and frustrations, such as dependency issues, breaking changes, compatibility problems, outdated documentation, etc. that can affect your development process and productivity.
If you are already comfortable with JavaScript and React, you might find React Native easier to work with than Flutter. If you are new to cross-platform development or looking for a more streamlined and integrated experience, you might prefer Flutter.
Flutter vs React Native: Ecosystem
Both Flutter and React Native have large and vibrant ecosystems that provide a wide range of tools, libraries, plugins, templates, etc. for extending and enhancing your app. However, there are some differences between them that can affect your choice:
- React Native has a larger and more mature ecosystem than Flutter. Since React Native has been around longer and has a larger user base, you can find more third-party libraries and community support for React Native than Flutter. If you need a specific functionality or integration that is not available in the core framework, you are more likely to find it in React Native’s ecosystem.
- Flutter’s ecosystem is growing rapidly and catching up with React Native’s. Despite being newer, Flutter has attracted a lot of attention and contributions from developers and companies around the world. Google is also investing heavily in Flutter and promoting it as the future of app development. This means that Flutter’s ecosystem is expanding and improving quickly, with new packages and updates being released regularly.
Flutter’s ecosystem is more cohesive and consistent than React Native’s. Since Flutter controls the entire rendering pipeline and provides a unified set of APIs and conventions, you can expect a more consistent and seamless experience when using third-party libraries or plugins in Flutter. React Native’s ecosystem is more fragmented and varied, with different libraries following different standards and practices.
Flutter vs React Native: Device Compatibility
When it comes to device compatibility, both Flutter and React Native provide good support for iOS and Android devices. However, there are some differences between them that can affect your choice:
– Flutter provides better support for newer and less common devices and platforms. Since Flutter uses its own rendering engine and does not rely on native UI components, it can support a wider range of devices and form factors, such as foldable phones, wearables, TVs, etc. Flutter also supports desktop and web development, which means you can use the same codebase for building apps on Windows, macOS, Linux, and the web.
– React Native focuses more on providing a native-like experience on iOS and Android devices. If you want your app to follow the native design guidelines and behavior of each platform, you might prefer React Native. React Native also has community support for other platforms such as Windows and macOS, but it is less comprehensive and official than Flutter’s support.Flutter vs React Native: Hiring and Cost
If you are a project manager or a business owner, you might be concerned about the availability and cost of developers for Flutter and React Native.
– React Native developers are generally easier to find and hire than Flutter developers. Since React Native uses JavaScript and React, which are widely used and taught languages and frameworks, you can find more developers with experience and expertise in React Native. Flutter developers might be less common and more specialized, especially if they have experience with Dart, which is less popular and familiar than JavaScript.
– The average hourly rate for a React Native developer might be slightly lower than a Flutter developer, especially in regions where JavaScript and React are more prevalent. However, the cost difference might not be significant, and it can vary depending on other factors such as the developer’s experience, location, portfolio, etc.Conclusion
Choosing between Flutter and React Native depends on your specific needs, preferences, and constraints. Both frameworks have their strengths and weaknesses, and both are capable of building high-quality cross-platform apps.
- If you prioritize performance, customization, developer experience, and future growth, you might prefer Flutter.
- If you prioritize community support, native-like experience, existing knowledge of JavaScript, and React, you might prefer React Native.
It’s always a good idea to try both frameworks, consult with experienced developers, and consider your project requirements before making a final decision. You might also consider other factors such as your team’s skillset, your target audience, your budget, your timeline, etc. that are unique to your situation.
In the end, both Flutter and React Native are powerful tools that have proven successful in the industry, and either choice can lead to a successful mobile app development project.
-
Offshore outsourcing
WHAT IS OFFSHORE OUTSOURCING?

Offshore outsourcing is the practice of hiring an external organization to perform some business functions in a country other than the one where the products or services are developed or manufactured. It is a form of outsourcing that uses a service provider that is not in the same country and often not on the same continent as the company paying for services. Offshore outsourcing can help businesses reduce costs, access specialized skills, and increase productivity and efficiency.
When to use offshore outsourcing?
Offshore outsourcing can be used for various business functions, such as IT, sales, customer service, accounting, marketing, human resources, and more. Some common examples of offshore outsourcing are:
- Software development: Many companies outsource software development projects to countries like India, China, or Eastern Europe, where there is a large pool of qualified programmers who can deliver high-quality work at lower rates than in-house developers.
- Call center: Many companies outsource their customer service or technical support operations to countries like the Philippines, Mexico, or South Africa, where there are skilled agents who can speak fluent English or other languages and handle customer inquiries efficiently and professionally.
- Data entry: Many companies outsource their data entry tasks to countries like India, Pakistan, or Bangladesh, where there are workers who can perform accurate and fast data entry at a fraction of the cost of domestic workers.
Advantages of offshore outsourcing
Offshore outsourcing can offer many benefits to businesses, such as:
- Cost savings: Offshore outsourcing can help businesses save up to 70% on labor costs, as well as reduce overhead expenses such as office space, equipment, taxes, and benefits. Offshore outsourcing can also help businesses avoid the costs of hiring, training, and retaining in-house staff.
- Quality improvement: Offshore outsourcing can help businesses access a wider talent pool of skilled and experienced workers who can deliver high-quality work that meets or exceeds the expectations of the clients. Offshore outsourcing can also help businesses leverage the best practices and technologies of the service providers.
- Productivity enhancement: Offshore outsourcing can help businesses increase their productivity and efficiency by allowing them to focus on their core competencies and strategic goals. Offshore outsourcing can also help businesses scale up or down their operations according to their needs and demand.
Disadvantages of offshore outsourcing
Offshore outsourcing can also pose some challenges and risks to businesses, such as:
- Communication barriers: Offshore outsourcing can create communication issues due to language differences, cultural differences, time zone differences, and lack of face-to-face interaction. These issues can affect the clarity, accuracy, and timeliness of the communication between the clients and the service providers.
- Quality control: Offshore outsourcing can make it difficult for businesses to monitor and control the quality of the work done by the service providers. There may be variations in the standards, expectations, and regulations of the different countries involved in the offshore outsourcing process.
- Security risks: Offshore outsourcing can expose businesses to security risks such as data breaches, intellectual property theft, or cyberattacks. Businesses need to ensure that they have adequate security measures and policies in place to protect their sensitive information and assets when they outsource them offshore.
Range of prices for offshore outsourcing
The prices for offshore outsourcing vary depending on several factors, such as:
- The type and complexity of the work
- The location and reputation of the service provider
- The skill level and experience of the workers
- The duration and scope of the project
- The quality standards and requirements of the client
According to some estimates, the average hourly rates for offshore outsourcing are:
- Software development: $25-$60
- Call center: $8-$15
- Data entry: $5-$10
Risks of offshore outsourcing
Some of the potential risks of offshore outsourcing are:
- Legal issues: Offshore outsourcing may involve different legal systems and regulations that may affect the contractual agreements, liabilities, disputes, and compliance issues between the clients and the service providers. Businesses need to ensure that they understand and follow the laws and regulations of both their own country and the country where they outsource their work.
- Cultural issues: Offshore outsourcing may involve different cultural norms and values that may affect the work ethics, behaviors, attitudes, and expectations of both the clients and the service providers. Businesses need to ensure that they respect and adapt to the cultural differences and avoid any misunderstandings or conflicts that may arise from them.
- Ethical issues: Offshore outsourcing may raise some ethical concerns regarding the social and environmental impacts of transferring work from one country to another. Businesses need to ensure that they adhere to ethical principles and practices when they outsource their work offshore.
Benefits of offshore outsourcing
Some of the potential benefits of offshore outsourcing are:
- Competitive advantage: Offshore outsourcing can help businesses gain a competitive edge in their market by allowing them to offer better quality, lower prices, faster delivery, or more innovation to their customers. Offshore outsourcing can also help businesses access new markets and opportunities by expanding their global presence and reach.
- Customer satisfaction: Offshore outsourcing can help businesses improve their customer satisfaction by providing them with more responsive, reliable, and customized services. Offshore outsourcing can also help businesses meet the diverse and changing needs and preferences of their customers by offering them more variety, flexibility, and convenience.
- Employee satisfaction: Offshore outsourcing can help businesses improve their employee satisfaction by reducing their workload, stress, and burnout. Offshore outsourcing can also help businesses enhance their employee skills, knowledge, and performance by providing them with more training, feedback, and support.
Examples of successful offshore outsourcing cases
Some of the examples of successful offshore outsourcing cases are:
- Google: Google is one of the leading companies that use offshore outsourcing for various functions, such as software development, data analysis, customer service, and content moderation. Google has outsourced some of its work to countries like India, China, Ireland, Poland, and the Philippines. Google has benefited from offshore outsourcing by reducing its costs, increasing its innovation, and improving its quality.
- Netflix: Netflix is another prominent company that uses offshore outsourcing for its customer service operations. Netflix has outsourced its customer service to countries like the Philippines, Brazil, Mexico, and Japan. Netflix has benefited from offshore outsourcing by enhancing its customer experience, expanding its global reach, and optimizing its resources.
- Slack: Slack is a popular communication platform that uses offshore outsourcing for its software development projects. Slack has outsourced some of its software development to countries like Ukraine, Canada, India, and Australia. Slack has benefited from offshore outsourcing by accessing specialized skills, accelerating its development process, and increasing its productivity.
Outsourcing is always an excellent choice if you have someone keeping in touch with the provider. Remember, you cannot have a baby, disappear, and then come back within 5 years and expect the baby to behave as you wish. Always keep an eye on your project, set up the right KPI to measure the process and provide continuous feedback over the relationship and the outcome you are getting from the outsourced company service.
-
SQL Server vs PostgreSQL: How to Choose the Right Database for Your Project
SQL Server vs PostgreSQL: How to Choose the Right Database for Your Project

If you are looking for a reliable and powerful database management system for your applications, you might be wondering whether to choose SQL Server or PostgreSQL. Both are popular and widely used SQL-based systems that offer many features and benefits for different use cases. However, they also have some key differences that you should consider before making a decision.
In this article, we will compare SQL Server and PostgreSQL in terms of their history, features, advantages, disadvantages, performance, scalability, security, and compatibility. We will also provide some tips on how to decide which one is the best fit for your project based on your requirements and preferences.
A Brief History of SQL Server and PostgreSQL
SQL Server is a proprietary database system developed by Microsoft. It was first released in 1989 as a joint project with Sybase and Ashton-Tate. Since then, it has evolved into a comprehensive platform that supports various data warehousing, business intelligence, transaction processing, data analytics, and machine learning services.
SQL Server has a row-based table structure that allows you to connect related data elements from different tables without having to store data multiple times in a database. It also supports various data types, such as XML, JSON, spatial, temporal, and graph data.
PostgreSQL is an open-source database system that originated from the Postgres project at the University of California, Berkeley. It was first released in 1996 as an extension of the Ingres database system. Since then, it has grown into a robust and versatile system that supports both relational (SQL) and non-relational (JSON) querying.
PostgreSQL is also known for its extensibility and customizability. You can create your own data types, functions, operators, indexes, and languages without having to recompile the database. You can also use various extensions to enhance the functionality of PostgreSQL, such as PostGIS for geospatial data, PL/Python for Python scripting, and pgAdmin for graphical administration.
Features of SQL Server and PostgreSQL
Both SQL Server and PostgreSQL share many core features that make them suitable for managing and querying enormous amounts of data. Some of these features are:
- ACID compliance: Both systems ensure the atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability of transactions.
- SQL support: Both systems support the standard SQL language for creating, manipulating, and retrieving data from tables.
- Indexing: Both systems allow you to create indexes on columns or expressions to speed up queries and enforce constraints.
- Views: Both systems allow you to create views that are virtual tables based on queries.
- Stored procedures: Both systems allow you to create stored procedures that are precompiled sets of SQL statements that can be executed with parameters.
- Triggers: Both systems allow you to create triggers that are actions that are executed automatically when certain events occur in the database.
- Foreign keys: Both systems allow you to create foreign keys that are constraints that link columns in different tables based on a common value.
- Subqueries: Both systems allow you to use subqueries that are queries nested within other queries.
- Joins: Both systems allow you to use joins that are operations that combine rows from two or more tables based on a common condition.
However, there are also some features that differentiate SQL Server and PostgreSQL in terms of their capabilities and functionalities.
Some of these features are:
- Data types: PostgreSQL supports more data types than SQL Server, such as arrays, ranges, enums, composite types, user-defined types, and geometric types. SQL Server supports some data types that PostgreSQL does not, such as hierarchyid, sql_variant, and table-valued parameters.
- Extensions: PostgreSQL supports more extensions than SQL Server that add additional features and functionalities to the database. For example, PostGIS adds support for geospatial data and operations, pgcrypto adds support for encryption and hashing functions, and hstore adds support for key-value pairs. SQL Server supports some extensions that PostgreSQL does not, such as PolyBase for querying external data sources like Hadoop or Azure Blob Storage.
- Partitioning: PostgreSQL supports more partitioning methods than SQL Server that allow you to divide large tables into smaller ones for better performance and management. For example, PostgreSQL supports range partitioning (based on a continuous range of values), list partitioning (based on a discrete list of values), hash partitioning (based on a hash function), and composite partitioning (based on a combination of methods). SQL Server supports only range partitioning (based on a continuous range of values) and hash partitioning (based on a hash function).
- Replication: PostgreSQL supports more replication methods than SQL Server that allow you to copy data from one database server to another for backup or load balancing purposes. For example, PostgreSQL supports logical replication (based on changes in individual rows), physical replication (based on changes in disk blocks), streaming replication (based on continuous transfer of changes), and logical decoding (based on extracting changes from the write-ahead log). SQL Server supports only transactional replication (based on changes in individual transactions), snapshot replication (based on periodic snapshots of data), and merge replication (based on merging changes from multiple sources).
- Full-text search: PostgreSQL supports more full-text search features than SQL Server that allow you to perform complex text queries on natural language data. For example, PostgreSQL supports stemming (reducing words to their root form), lemmatization (reducing words to their canonical form), synonyms (using alternative words with the same meaning), thesaurus (using related words with different meanings), and phrase search (matching exact sequences of words). SQL Server supports only stemming, synonyms, and phrase search.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SQL Server and PostgreSQL
Both SQL Server and PostgreSQL have their own advantages and disadvantages that you should weigh before choosing one for your project. Some of these are:
- Cost: PostgreSQL is free and open-source, which means you do not have to pay any licensing fees or royalties to use it. You can also modify and distribute it as you wish. SQL Server is proprietary and licensed by Microsoft, which means you have to pay for the edition and features you want to use. You also have to abide by the terms and conditions of the license agreement.
- Support: PostgreSQL has a large and active community of users and developers who provide support and assistance through various channels, such as mailing lists, forums, blogs, wikis, and IRC. You can also find many online resources, tutorials, books, and courses on PostgreSQL. SQL Server has a dedicated support team from Microsoft who provide technical support and assistance through various channels, such as phone, email, chat, web, and forums. You can also find many online resources, tutorials, books, and courses on SQL Server.
- Compatibility: PostgreSQL is compatible with most operating systems, such as Linux, Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, Solaris, and others. You can also use PostgreSQL with most programming languages, such as C#, Java, Python, Ruby, PHP, Perl, and others. You can also use PostgreSQL with most frameworks and tools, such as Django, Rails, Laravel, Hibernate, and others. SQL Server is compatible only with Windows operating system. Also, consider that you can containerize your database too. You can also use SQL Server with most programming languages, such as C#, Java, Python, Ruby, PHP, Perl, and others. You can also use SQL Server with most frameworks and tools, such as .NET, Entity Framework, Spring Boot, and others.
- Performance: PostgreSQL is known for its high performance and scalability when handling complex queries and large workloads. It also supports various optimization techniques, such as parallel query processing, just-in-time compilation, and index-only scans. SQL Server is also known for its high performance and scalability when handling large workloads. It also supports various optimization techniques, such as query store, adaptive query processing, and columnstore indexes.
- Security: PostgreSQL supports various security features, such as encryption at rest and in transit, role-based access control, row-level security, audit logging, and certificate authentication. SQL Server also supports various security features, such as encryption at rest and in transit, role-based access control, row-level security, audit logging, and transparent data encryption.
How to Choose Between SQL Server and PostgreSQL
There is no definitive answer to which database system is better than the other. It depends on your project requirements, preferences,
and budget. However, here are some general guidelines that can help you make an informed decision:Choose PostgreSQL if you want a free and open-source database system that supports both relational and non-relational data types, has more extensibility and customizability options,
has more partitioning and replication methods, has more full-text search features,
and is compatible with most operating systems.Choose SQL Server if you want a proprietary and licensed database system that has more data warehousing, business intelligence, data analytics, and machine learning services, has more extensions for querying external data sources, has more dedicated support from Microsoft, and is compatible only with Windows operating system.
Of course, these are not the only factors that you should consider when choosing a database system. You should also evaluate other aspects such as ease of use, learning curve, documentation quality, availability of tools, community size, and future development plans.
Ultimately, the best way to choose between SQL Server and PostgreSQL is to try them out yourself. You can download and install both systems on your local machine or use cloud-based services that offer them as a service. You can then test them with your own data and queries
and compare their performance, functionality, and usability.We hope this article has helped you understand the differences between SQL Server and PostgreSQL and how to choose the right database for your project.
-
SQL Server vs SQL Express: A Comparison
SQL Server vs SQL Express: A Comparison

SQL Server and SQL Express are both relational database management systems (RDMS) developed by Microsoft. They share many features and capabilities, but they also have some important differences. In this article, we will compare SQL Server and SQL Express in terms of when to use them, what kind of applications they support, how many concurrent users they can handle, and what are the advantages and disadvantages of each one over the other.
When to use SQL Server or SQL Express?
SQL Server is the premium offering that delivers comprehensive data management and business intelligence solutions for enterprise-level workloads. SQL Server is suitable for mission-critical applications that require high performance, scalability, availability, security, and advanced analytics. SQL Server also supports unlimited virtualization, cloud integration, and end-user access to data insights.
SQL Express is the entry-level, free edition that is ideal for learning and building desktop and small server applications. SQL Express is suitable for small to medium-sized businesses that need a basic data management and reporting solution. SQL Express also supports common development tools for on-premises and cloud environments, enabling effective database management with minimal IT resources.
What kind of applications can SQL Server or SQL Express support?
SQL Server can support any kind of application that requires a robust and reliable RDMS. SQL Server can handle complex queries, large volumes of data, multiple concurrent transactions, and sophisticated analytics. SQL Server can also integrate with various data sources, such as other databases, files, web services, or big data platforms. SQL Server can also provide rich reporting and visualization tools, such as Power BI, to enable data-driven decision making.
SQL Express can support simple applications that require a lightweight and easy-to-use RDMS. SQL Express can handle basic queries, moderate amounts of data, limited concurrent transactions, and simple analytics. SQL Express can also connect to other databases or files, but with some restrictions on the size and number of databases. SQL Express can also provide basic reporting and visualization tools, such as Report Builder or SSRS, to enable data exploration.
How many concurrent users can SQL Server or SQL Express handle?
SQL Server can handle thousands of concurrent users without compromising performance or availability. SQL Server can scale up by using more powerful hardware resources, such as CPU cores, memory, or disk space. SQL Server can also scale out by using distributed architectures, such as clustering, replication, or partitioning. SQL Server can also leverage in-memory technologies, such as columnstore indexes or memory-optimized tables, to boost query speed and concurrency.
SQL Express can handle up to 32 concurrent users with acceptable performance and availability. SQL Express has some limitations on the hardware resources it can use, such as 1 CPU core, 1 GB of memory, or 10 GB of disk space per database. SQL Express does not support distributed architectures or in-memory technologies. Therefore, SQL Express may experience performance degradation or resource contention when the number of users or the size of data increases.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of SQL Server or SQL Express over each other?
SQL Server has the following advantages over SQL Express:
- It offers more features and functionalities to meet diverse business needs.
- It delivers higher performance and scalability to support larger workloads.
- It provides better availability and reliability to ensure business continuity.
- It enables more advanced analytics and insights to drive business value.
SQL Server has the following disadvantages compared to SQL Express:
- It requires a license fee that depends on the edition and the number of cores used.
- It demands more IT expertise and maintenance to manage the system.
- It may have compatibility issues with some older applications or platforms.
SQL Express has the following advantages over SQL Server:
- It is free to download and use for any purpose.
- It is easy to install and configure with minimal IT skills.
- It is compatible with most applications and platforms that support SQL Server.
SQL Express has the following disadvantages compared to SQL Server:
- It has fewer features and functionalities to meet complex business needs.
- It has lower performance and scalability to support larger workloads.
- It has less availability and reliability to ensure business continuity.
- It offers less advanced analytics and insights to drive business value.
Conclusion
SQL Server and SQL Express are both powerful RDMS that can support various applications and scenarios. However, they also have some significant differences that should be considered before choosing one over the other. In general, SQL Server is more suitable for enterprise-level applications that require high-end data management and business intelligence solutions. On the other hand, SQL Express is more suitable for small-scale applications that require basic data management and reporting solutions.
-
Choosing the Right Technology for API Development
Choosing the Right Technology for API Development
Selecting the right technology for API development is crucial. In this article, we will explore five key technologies, namely PHP, .NET, Golang, Python, Ruby on Rails, and Java, and understand the ideal scenarios for each.
PHP
History
PHP, or Hypertext Preprocessor, was created by Rasmus Lerdorf in 1994. Originally designed for managing personal web pages, it has evolved into a server-side scripting language widely used in web development.

Advantages
- Easy to learn and use
- Wide hosting support
- Strong community support
- Flexible for web development
Disadvantages
- Not as suitable for large-scale applications
- Lacks modern development features compared to other languages
Ideal Scenario
PHP is best suited for small to medium-scale web applications and websites, particularly where rapid development and cost-effectiveness are priorities. https://successjourneychallenge.wordpress.com/backend-language-battle-part-4-php/
.NET
History
.NET was developed by Microsoft and released in 2002. It has since become a popular platform for building Windows applications and web services.
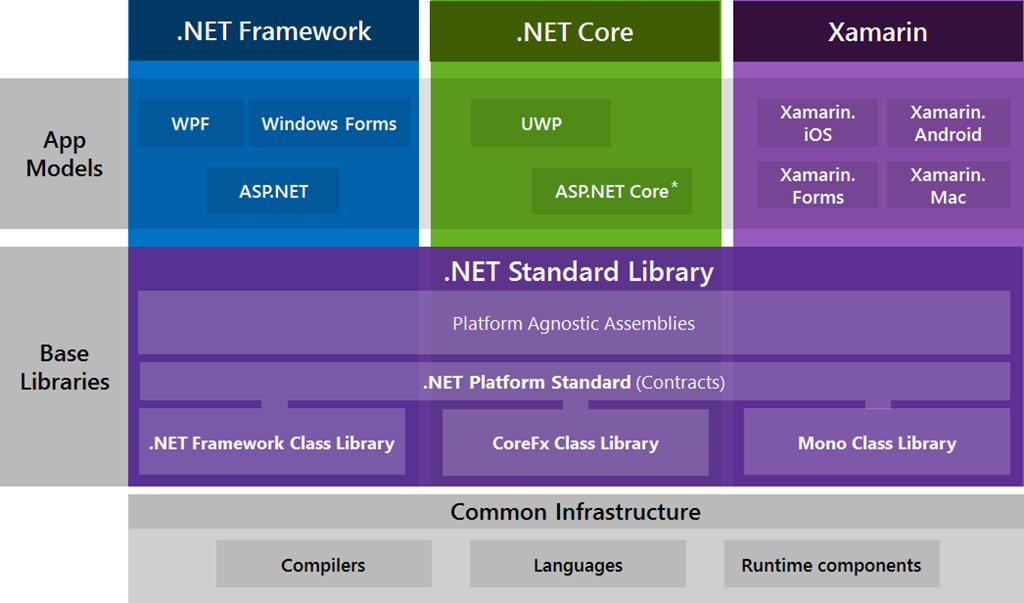
Advantages
- Rich set of libraries and tools
- Seamless integration with Microsoft products
- Cross-platform development with .NET Core
- Strong performance
Disadvantages
- Can be expensive due to licensing costs
- May have a steeper learning curve for beginners
Ideal Scenario
.NET is optimal for large-scale applications, particularly in enterprise environments that leverage Microsoft technologies. https://successjourneychallenge.wordpress.com/unlocking-the-power-of-backend-development-a-comprehensive-guide-to-choosing-the-right-language-for-your-apis/
Golang
History
Developed at Google, Golang or Go was designed to simplify development without sacrificing performance. Released in 2009, it’s known for its simplicity and efficiency in concurrency handling.

Advantages
- Simple and easy to maintain
- Efficient concurrency handling
- Quick compilation and execution
Disadvantages
- Lacks some features and libraries found in older languages
- Less suitable for UI development
Ideal Scenario
Go is best suited for performance-critical applications, microservices architecture, and scalable network servers. https://successjourneychallenge.wordpress.com/backend-language-battle-part-3-golang/
Ruby on Rails
History
Ruby on Rails, or Rails, is a web application framework written in Ruby. Created by David Heinemeier Hansson, it was first released in 2005 and emphasizes convention over configuration.
Advantages
- Speeds up development
- Rich libraries and community support
- Flexible and customizable
Disadvantages
- May not be as performant as other languages
- Can be less suitable for large-scale complex applications
Ideal Scenario
Ruby on Rails is ideal for startups and small to medium-scale web applications where rapid development is a key requirement.
https://successjourneychallenge.wordpress.com/backend-language-battle-part-5-ruby-on-rails/
Python
Since its creation in 1991, Python has become a favorite for its readability and versatility, especially in data science and machine learning.
Python’s widespread popularity in the field of data science and machine learning makes it an attractive choice for applications that require heavy data processing, analysis, and predictive functionalities. https://successjourneychallenge.wordpress.com/backend-language-battle-part-2-python/

Advantages
- Readable syntax
- Rich libraries
- Strong community support
Disadvantages
- Slower performance
- Memory consumption
Java
History
Java was developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems and released in 1995. Known for its “Write Once, Run Anywhere” capability, it’s widely used in enterprise applications, Android development, and more.

https://successjourneychallenge.wordpress.com/backend-language-battle-part-6-java/
Advantages
- Platform independence
- Robust performance
- Rich ecosystem and libraries
- Strong community support
Disadvantages
- Can be verbose
- Higher memory consumption
Ideal Scenario
Java is suited for large-scale enterprise applications, Android development, and systems that require platform independence.
Conclusion
Each of the above technologies has its own unique strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different scenarios. Understanding your project’s specific requirements, scalability needs, budget constraints, and development timelines will guide your choice.
In summary, PHP is great for rapid web development, .NET for enterprise solutions, Go for performance-critical systems, Ruby on Rails for rapid and flexible development, and Java for platform-independent, large-scale applications. The right choice will align with your project’s unique needs and maximize its success.
-
Backend language battle part 6 – Java
Choosing Java for API Development: An Expert’s Guide

As an expert in PHP, .NET, Go, Ruby on Rails, and Java, I’ve explored various technologies to suit different needs. In this article, I’ll explain why Java stands out as a premier choice for API development and illustrate the scenarios in which it excels.
Advantages of Java for API Development
1. Platform Independence:
Java’s mantra, “Write Once, Run Anywhere,” holds true. Compiled Java code runs on any system with a JVM, offering significant flexibility and portability.
2. Robustness and Security:
Java’s strong typing, exception handling, and garbage collection features contribute to robust applications. Additionally, Java’s security model offers protection against various threats.
3. Scalability:
Java’s concurrency support and performance optimizations enable it to scale effectively for large applications, handling substantial user loads with ease.
4. Extensive Libraries:
Java boasts a rich ecosystem of libraries and frameworks (e.g., Spring) that speed up development and integrate smoothly with various services.
Disadvantages of Java for Backend API Development
While Java is a robust and widely used programming language, there are specific scenarios where other languages might be more suitable for backend API development. In this article, we’ll explore some of the disadvantages of Java compared to .NET, PHP, Ruby on Rails, and Golang.
Disadvantages of Java
1. Verbosity:
Java is often criticized for its verbosity. Writing simple functionalities might require more lines of code compared to languages like Ruby on Rails or Python. This can lead to longer development times.
2. Memory Consumption:
Java applications can be more memory-intensive compared to languages like Golang, which may impact the efficiency and scalability of the API.
3. Slower Startup Time:
Java’s slower startup time, especially in large applications, may not be as optimal as the quick startup time seen in languages like Golang.
4. Less Flexibility in Web Development:
Languages like PHP and Ruby on Rails may offer more built-in functionalities specifically tailored for web development, potentially reducing development time and complexity.
Comparison with Other Technologies
Compared to .NET:
.NET may offer better integration with other Microsoft products and may be a preferred choice for Windows-centric environments.
Compared to PHP:
PHP’s web-centric design and extensive hosting support might make it a more attractive choice for lightweight web applications.
Compared to Ruby on Rails:
Ruby on Rails’ convention over configuration approach can significantly speed up the development process compared to Java.
Compared to Golang:
Golang’s simplicity, efficiency in concurrency handling, and lower memory consumption may make it a more attractive option for performance-critical applications.
Scenarios Where Java is the Best Choice
1. Enterprise Applications:
Java’s reliability, security, and scalability make it the go-to choice for large-scale enterprise applications where performance and stability are paramount.
2. Cross-Platform Solutions:
If you require a solution that runs across various platforms without modification, Java’s platform independence is unmatched.
3. Integrations with Existing Systems:
Java’s mature ecosystem facilitates smooth integration with existing systems and third-party services, simplifying complex projects.
Conclusion
While PHP, .NET, Go, and Ruby on Rails each have their distinct benefits, Java shines in scenarios demanding robustness, security, scalability, and cross-platform capability. Its extensive libraries and frameworks simplify development, while platform independence ensures your API will function seamlessly across different environments.
Java’s longstanding reputation as a versatile and reliable programming language makes it an excellent choice for many API development projects, from small startups to large enterprises. Careful evaluation of your project’s specific needs will guide you in making the most informed technology decision, but in many cases, Java’s proven strengths make it an outstanding candidate.
-
Subscribe
Subscribed
Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.